Introduction
Cybersecurity in Healthcare Statistics: As the healthcare sector increasingly integrates digital technologies, the need for robust cybersecurity measures has become more critical than ever. Adopting electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, and connected medical devices has significantly enhanced patient care and operational efficiency.
However, this digital shift has also exposed healthcare organizations to a rising tide of cyber threats, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, and hacks of medical devices. The sensitive nature of the data fuels these threats, such as personal health information (PHI) and payment records, making healthcare one of the most targeted cyberattack industries.
In response to these growing risks, healthcare providers must prioritize implementing stringent cybersecurity policies and embrace cutting-edge technologies like encryption, artificial intelligence, and multi-factor authentication. The sector is grappling with challenges such as outdated security systems, inadequate staff training, and the complexities of safeguarding networks of interconnected devices.
As cyberattacks become more frequent and sophisticated, understanding cybersecurity statistics within healthcare is essential for identifying vulnerabilities, assessing risks, and strengthening defenses to protect sensitive patient data and maintain trust within the industry.
Editor’s Choice
- The frequency of data breaches within healthcare organizations saw a sharp 50% increase compared to the previous year, underscoring the rising threat to patient data.
- A recent survey found that nearly 66% of healthcare providers were targeted by cyberattacks over the past year.
- Internal threats, such as employee errors or intentional misconduct, caused more than 74% of data breaches in healthcare.
- On average, resolving a data breach in healthcare costs over $9.77 million, covering fines, legal expenses, and reputational repair.
- In response to escalating cyberattacks, healthcare organizations raised their cybersecurity budgets by 25% year-over-year.
- As healthcare adopts more digital solutions, the risk of cyberattacks, including data breaches, ransomware, and the hacking of medical devices, has significantly increased.
- The continuous evolution of cyber threats has intensified the need for cutting-edge cybersecurity technologies to protect sensitive healthcare data.
- The growing threat environment drives the widespread implementation of stronger encryption methods and multi-factor authentication to ensure patient data security.
- The healthcare sector is increasingly utilizing artificial intelligence-powered security tools to address more complex and advanced cyber threats.
(Source: ASTRA IT, Inc., Breachsense)
Healthcare Cybersecurity Market Size
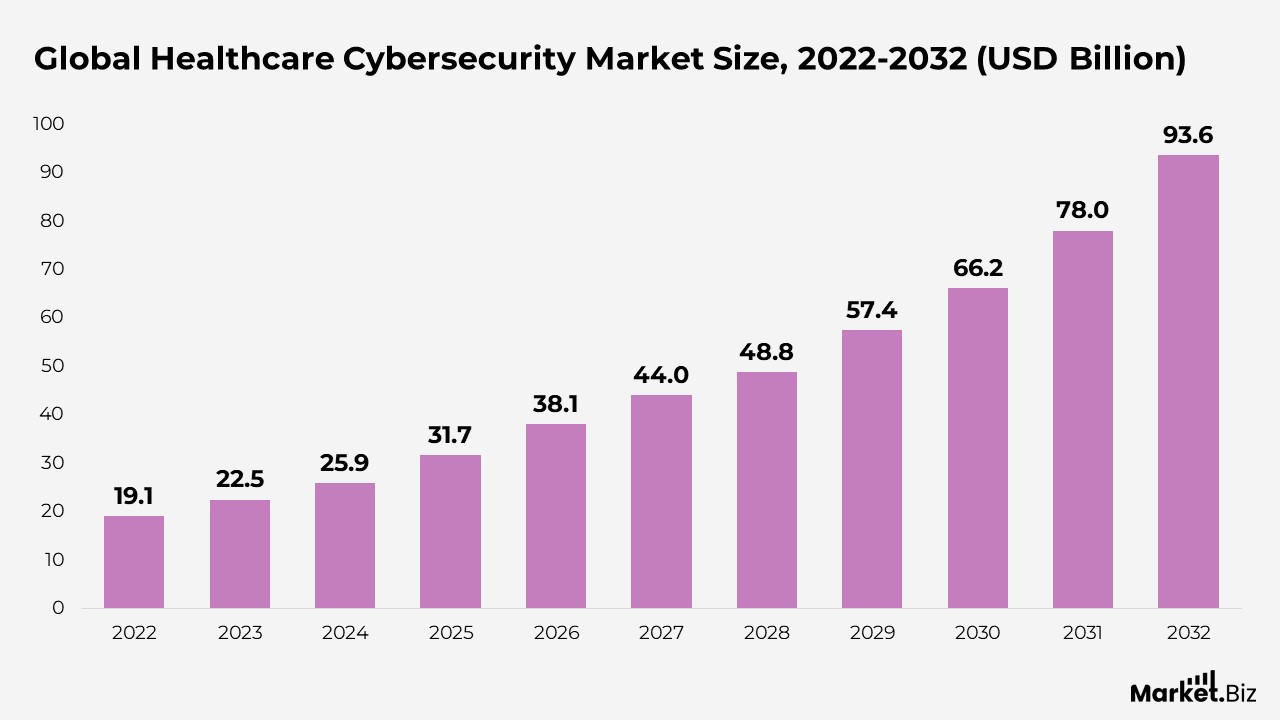
- As per Market.us, the global market for healthcare cybersecurity is anticipated to expand from $31.7 billion in 2025 to $93.6 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.7% from 2022 to 2032.
- The healthcare cybersecurity market is expanding due to the rising demand for cybersecurity solutions, the surge in cyberattacks targeting healthcare organizations, digital transformation in healthcare, and technological advancements in security solutions.
- The malware and spyware segment holds the largest market share, as these threats compromise patient privacy and system integrity. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks also hinder healthcare professionals’ ability to provide high-quality patient care.
- Cloud-based deployment is the leading mode for healthcare cybersecurity solutions, allowing organizations to scale their security measures more efficiently and reduce upfront costs. However, this deployment model raises concerns regarding data privacy and security.
- The solutions segment is expected to capture the largest share of the healthcare cybersecurity market, driven by the increasing need for advanced security operations, rising data security concerns, and the demand for reliable, cost-effective security solutions to strengthen cybersecurity infrastructure.
- The cloud security segment is growing at the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR), fueled by the increasing use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the growing volume of sensitive data within the healthcare industry.
- Healthcare payers represent the largest revenue share in the market, supported by increasing awareness of electronic health records, heightened data security concerns, and government initiatives and regulations aimed at protecting patient data from cyber threats.
- North America holds over 41% of the market share for healthcare cybersecurity, with major companies and healthcare organizations’ growing adoption of cybersecurity solutions driving market growth. Investments in technology advancements and the development of healthcare infrastructure are key factors contributing to this dominance.
(Source: Market.us)
Healthcare Data Breaches
Healthcare data breaches continue to pose a major threat, as the increasing volume of sensitive patient data attracts the attention of cybercriminals. These breaches can have far-reaching consequences for individuals and healthcare organizations, including the exposure of confidential health data, financial repercussions, and damage to reputation.
- 2023 healthcare data breaches affected over 540 organizations and 112 million individuals, as reported to the HHS Office for Civil Rights (OCR), compared to 590 organizations and 48.6 million individuals in 2022.
- In January 2024, 24 breaches were reported, each involving over 10,000 records, including one that exposed 500,000 records and another that impacted more than 2 million.
- The largest breach compromised 11.27 million records, while another major breach affected 4 million in 2023.
- According to HIPAA, there has been a 48% reduction in healthcare data breaches in the U.S. However, this drop should not be mistaken for a complete resolution, as the sector still faces significant cybersecurity risks.
- Around 36% of healthcare facilities have reported an uptick in medical complications due to ransomware attacks, highlighting the critical effect of cyber threats on patient care and medical outcomes.
Moreover
- Despite the escalating cyber risks, only 4-7% of the IT budgets of healthcare organizations are allocated to cybersecurity. This limited funding leaves many healthcare systems vulnerable to attacks and data breaches.
- Internal threats remain a primary cause of healthcare data breaches, with 61% of incidents stemming from employee negligence. This includes errors such as mishandling sensitive data or falling prey to phishing scams.
- The healthcare sector experienced nearly 337 data breaches in the first half of 2022, according to Fortified Health Security. This underscores the persistent frequency of cyber incidents within the healthcare industry.
- The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services reported that these 337 breaches affected nearly 20 million individuals, demonstrating the large-scale nature of data exposure in these incidents.
- A significant 80% of healthcare breaches in the U.S. are attributed to hacking, emphasizing the growing trend of cybercriminals targeting healthcare organizations for sensitive data. Unauthorized access constitutes the remaining 15%, further highlighting the need for enhanced security measures within healthcare systems..
(Source: ASTRA IT, Inc., TechTarget, Inc. The HIPAA Journal)
Cybersecurity Coverage and Premiums
- In the past year, large organizations faced a 46% increase in cyber insurance premiums, reflecting the growing risk and costs associated with cyber threats.
- Medium-sized businesses also experienced a notable 50% rise in cyber insurance premiums, underscoring the broader impact of cybersecurity challenges across organizations of all sizes.
- Only 52% of Healthcare Delivery Organizations (HDOs) include medical device security in their insurance policies, highlighting a gap in coverage for critical healthcare infrastructure.
- HDOs with a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) overseeing medical device security report an 18% increase in their Healthcare Industry Cybersecurity Practices (HICP) coverage, demonstrating the importance of dedicated leadership in improving security posture.
- Under the leadership of a CISO, HICP coverage in healthcare organizations improved from 45% to 63%, reflecting the positive impact of executive oversight on enhancing cybersecurity practices.
(Source: Market.us, Offensive Security Services)
Cybersecurity Investment and Resource Distribution
- Biden administration allocates $800 million for hospital cybersecurity: As part of its 2025 budget, the Biden administration has proposed an $800 million investment to bolster cybersecurity measures in hospitals.
- Healthcare sector to invest $125 billion in cybersecurity by 2025: From 2020 to 2025, the healthcare industry is projected to invest $125 billion in cybersecurity solutions, reflecting a consistent 15% annual growth in spending.
- Blockchain adoption drives $5.61 billion cybersecurity expenditure by 2025: By 2025, the healthcare sector’s cybersecurity spending is expected to reach $5.61 billion, fueled largely by the growing implementation of blockchain technology.
- Healthcare cybersecurity budgets see 12% growth in 2024: Cybersecurity budgets in the healthcare industry grew by 12%, averaging $66 million in 2024, with nearly 19% allocated specifically to information security initiatives.
(Source: dialog health)
Financial and Insurance Implications
- In 2024, 67% of healthcare organizations were targeted by ransomware attacks, increasing from 60% in 2023 to nearly double the 34% reported in 2021 nearly nearly nearly.
- Only 47% of ransomware payments made by healthcare organizations were covered by cybersecurity insurance policies.
- Healthcare organizations incurred an average recovery cost of $2.57 million due to ransomware attacks in 2024, up from $2.2 million in 2023.
- Healthcare organizations with compromised backups faced a median recovery cost of $750,000, double the $375,000 cost for those with secure backups.
- In 2024, only 22% of ransomware victims in healthcare fully recovered within a week or less, a significant drop from 47% in 2023 and 54% in 2022.
- The percentage of healthcare organizations requiring more than a month to recover from ransomware attacks rose to 37% in 2024, up from 28% in 2023..
(Source: dialog health)
Cybersecurity Training, Policies, and Incident Response in Healthcare
- Over 75% of healthcare employees have reported undergoing cybersecurity awareness training, reflecting an effort to equip staff with the knowledge to mitigate cyber risks.
- Despite the training efforts, 25% of healthcare workers who recognized the need for cybersecurity training were not provided with any, highlighting a gap in addressing the training needs of critical staff.
- 41% of healthcare providers regularly simulate phishing attacks as part of their cybersecurity training, aiming to raise awareness about the sector’s most common types of cyber threats.
- Nearly half (48%) of healthcare providers have incorporated phishing attack prevention and response measures into their cybersecurity strategies, showcasing an active approach to counteracting one of the most prevalent cyber threats.
- Only 37% of hospitals conduct annual cybersecurity incident response drills, indicating that many institutions may not be adequately prepared for responding to a cyberattack.
- Just 50% of healthcare organizations perform regular cybersecurity audits, revealing that many are not consistently evaluating and improving their security posture.
(Source: dialog health)
Vulnerabilities in the Healthcare Sector
- In 2023, 88% of healthcare organizations reported experiencing at least one cyberattack, with an average of 40 attacks occurring annually.
- Hacking was responsible for 80% of all data breaches in 2023, underscoring the persistent threat posed by cybercriminals targeting healthcare systems.
- Cyber incidents worldwide saw a dramatic increase from 32 in 2022 to 121 in 2023, with the European Repository of Cyber Incidents highlighting a notable surge in attacks specifically directed at the healthcare sector.
(Source: Market.us, Healthcare Dive, Market.us)
Training and Workforce Issues
- As of July 2022, the healthcare industry reported a shortage of 78,000 staff members compared to February 2020.
- From 2020 to 2030, the healthcare sector will require an additional 275,000 nurses, with nursing employment expected to grow by 9% between 2016 and 2026.
- 61% of healthcare cybersecurity professionals identify staff shortages as the primary obstacle to strengthening cybersecurity measures.
- 84% of healthcare organizations struggle to attract qualified cybersecurity professionals due to the high demand and competitive market.
- 67% of healthcare organizations report difficulties in retaining skilled cybersecurity professionals.
- 55% of healthcare organizations face budget limitations that hinder their ability to hire necessary cybersecurity staff, while 43% cite non-competitive compensation as a challenge…
(Source: Market.us)
Emerging Trends
- The rapid integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) into healthcare systems has introduced benefits and challenges. These technologies are essential for remote monitoring and data collection, but also create new vulnerabilities. The growing number of connected devices adds complexity to securing each endpoint from cyber threats, presenting a significant challenge for IT security teams.
- Blockchain is emerging as a powerful tool for enhancing cybersecurity in healthcare. While it’s widely known for securing financial transactions, its application in healthcare offers stronger data protection and privacy. Blockchain ensures the integrity and traceability of patient records, providing an effective defense against data manipulation and unauthorized access.
- With healthcare providers’ increasing reliance on cloud computing, robust cloud security has become a priority. This includes implementing advanced penetration testing, data loss prevention measures, and end-to-end encryption. These strategies are critical to safeguarding sensitive patient information from cyber threats like phishing and malware attacks.
- The healthcare sector remains a key target for ransomware attacks due to the critical nature of its services. To address this risk, healthcare organizations focus on continuous vulnerability assessments, enforcing strict access controls, and developing comprehensive incident response plans. These initiatives are designed to minimize the impact of cyberattacks and ensure the continuity of services.
- Healthcare organizations are increasingly adopting biometric authentication to enhance security protocols. Using unique biological identifiers like fingerprints or facial recognition, biometric systems offer a more secure and user-friendly alternative to traditional password-based access methods.
- Navigating the complex regulatory landscape, including HIPAA and the FTC Act laws, is critical for healthcare organizations. Compliance not only protects patient data but also helps avoid legal repercussions. As data privacy regulations evolve, healthcare providers must remain vigilant and adaptable to maintain compliance and secure sensitive information..
(Source: Market.us, ScienceDirect, National Institute of Health)
Recent Developments
New Product Launches
- In November 2024, Health Catalyst, Inc. introduced BluePrint Protect, an AI-powered cybersecurity platform designed to identify and assess risks associated with third-party cybersecurity threats.
- In May 2024, the HHS agency rolled out a new cybersecurity initiative to automate hospital cybersecurity processes..
Use Cases
- With the growth of telehealth services, ensuring the security of these platforms has become critical. Healthcare providers must implement secure communication channels and strong authentication protocols to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive patient data from breaches. Securing telehealth services ensures compliance with regulations and fosters trust with patients who depend on these remote services for their healthcare needs.
- As the use of connected medical devices increases, robust cybersecurity measures are essential. Healthcare facilities must adopt regular software updates and comprehensive risk assessments to protect devices and data from cyber threats. These protocols are vital to maintaining patient safety and ensuring the reliable operation of medical devices..
Conclusion
Cybersecurity in Healthcare Statistics: Cybersecurity remains a critical challenge in healthcare as the industry embraces digital transformation. With the increasing adoption of telehealth services, connected medical devices, and cloud computing, the attack surface for cyber threats continues to expand.
The statistics reveal that healthcare organizations face growing cyberattacks, with ransomware and data breaches posing significant risks to patient safety and organizational integrity. While the sector has made strides in enhancing cybersecurity measures, such as investing in AI-driven solutions and improving incident response protocols, gaps in staff training, cybersecurity budgets, and retention of skilled professionals persist.
As the threat landscape evolves, it is essential for healthcare organizations to continuously update their cybersecurity strategies, invest in robust security infrastructure, and ensure compliance with ever-changing regulatory requirements. Strengthening healthcare cybersecurity is crucial for protecting sensitive patient data and maintaining trust, improving care quality, and safeguarding the industry against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
FAQ’s
Cybersecurity is essential in healthcare to protect sensitive patient information, maintain medical records’ accuracy, and preserve healthcare services’ confidentiality. Cybercriminals often target healthcare organizations due to the high value of healthcare data and the essential nature of healthcare operations.
Healthcare faces several key cybersecurity threats, including ransomware, phishing scams, data breaches, and attacks on connected medical devices. These risks can lead to unauthorized data access, interruptions, and significant financial losses.
To mitigate ransomware risks, healthcare organizations should implement regular software updates, conduct thorough vulnerability assessments, apply strong encryption, enforce strict access controls, and have a well-defined incident response plan. Ongoing staff training on phishing prevention and data protection practices is vital.
While connected medical devices enhance patient care through remote monitoring, they also introduce new cybersecurity risks. Healthcare providers should perform routine security evaluations, ensure timely updates to device software, and establish robust protocols to manage devices and secure data transmissions.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming an integral part of healthcare cybersecurity by helping organizations detect and respond to cyber threats more efficiently. AI-powered tools can analyze data patterns to anticipate and prevent potential security breaches, adding a proactive layer of protection against evolving threats.
Healthcare organizations often struggle to recruit skilled cybersecurity professionals due to high demand and stiff competition from other industries. Budget limitations and uncompetitive compensation packages further complicate the ability to attract and retain top-tier cybersecurity experts.
