Introduction
Hearing Loss Statistics: Hearing loss is a widespread and often overlooked health issue that affects millions of people of all ages globally. As a sensory impairment, it impacts communication and quality of life while also leading to social isolation, reduced productivity, and mental health issues.
Understanding the prevalence and patterns of hearing loss through accurate and current statistics is crucial for shaping effective public health policies. Increasing awareness and promoting early intervention.
This section provides key statistical insights into the global and regional burden of hearing loss, emphasizing risk factors, demographic trends, and the increasing demand for accessible hearing care services.
Editor’s Choice
- Noise exposure, particularly in industrialized countries, primarily contributes to hearing loss, followed by genetic predispositions, aging, certain medications, infections, and physical damage to the ear.
- Technological advancements in hearing aids and cochlear implants are transforming the lives of people with hearing loss. Enhancing communication and improving social interaction.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 1.5 billion people worldwide live with hearing loss, accounting for 20% of the global population. This number is expected to grow as the population ages and environmental noise exposure increases.
- The likelihood of hearing loss rises significantly with age. It is projected that one-third of individuals over 65 will experience some form of hearing impairment, with more than half of those over 75 affected.
- Deaf individuals face a substantial employment gap, with the disparity between deaf and hearing individuals in the U.S. reaching 22.5%, highlighting a critical issue in workforce inclusion and accessibility.
Global Hearing Aids Market Size
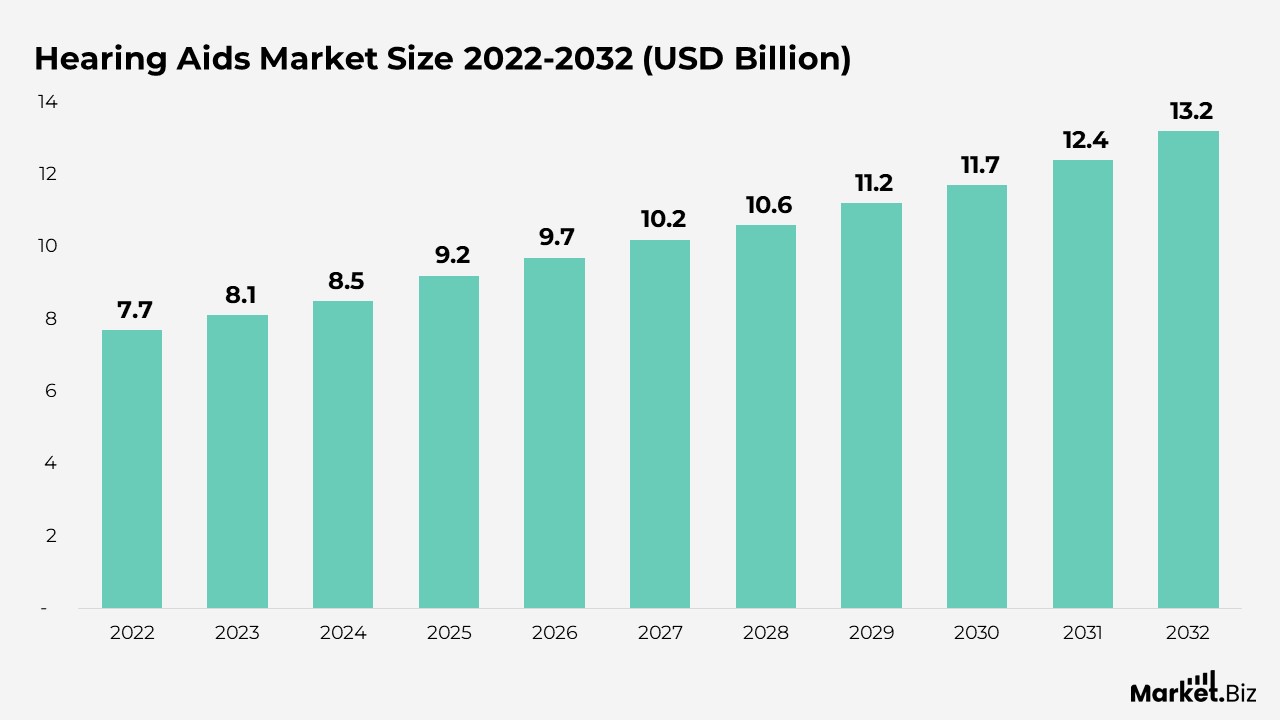
- As per Market.us, the global hearing aids market is projected to grow from $9.2 billion in 2025 to $13.2 billion by 2033. Reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% during the forecast period from 2022 to 2032.
- Market growth is driven by rising noise pollution and an aging population, particularly those prone to hearing loss.
- The Behind-The-Ear (BTE) hearing aids segment accounted for over 40% of revenue in 2022, fueled by Bluetooth compatibility and wireless connectivity.
- Retail sales, particularly over-the-counter hearing aids. Held over 70% of revenue in 2022 and are expected to grow fastest during the forecast period.
- North America leads the global hearing aids market, supported by increased research, smaller aesthetic devices, new product launches, and government support.
(Source: Market.us)
Types of Hearing Loss

(Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC))
Causes of Hearing Loss and Deafness
While hearing loss can occur at any stage of life, individuals are particularly vulnerable during key developmental periods.
Prenatal Period
- Genetic factors, including both hereditary and non-hereditary hearing loss
- Intrauterine infections, such as cytomegalovirus and rubella
Perinatal period
- Low-birth weight
- Hyperbilirubinemia (Severe jaundice in newborns)
- Birth asphyxia (oxygen deprivation during birth)
- Other complications during the perinatal period and their management
Adolescence and Childhood
- Fluid accumulation in the ear (chronic nonsuppurative otitis media)
- Chronic ear infections (chronic suppurative otitis media)
- Meningitis and other infections
Adulthood and older age
- Smoking
- Chronic diseases
- Age-related sensorineural hearing loss
- Otosclerosis
- Sudden sensorineural hearing loss
(Source: World Health Organization)
Global Hearing Loss Statistics
- Hearing loss is increasing worldwide, primarily driven by population growth, an aging demographic, exposure to loud noises, and the prevalence of preventable conditions like ear infections and certain diseases. Additionally, conditions like otitis media, viral infections, and diabetes can contribute to hearing loss.
- By 2024, more than 430 million people, including 34 million children, will require rehabilitation for disabling hearing loss. It is projected that by 2050, over 700 million people, or 1 in 10, will experience disabling hearing loss.
- Around 50% of hearing loss cases are believed to be preventable through effective public health interventions.
- Hearing loss severity is measured in decibels (dB). Ranging from normal hearing (0-25 dB) to profound loss (91+ dB).
- Over 1 billion young adults are at risk of permanent and avoidable hearing loss due to unsafe listening practices.
- Legal deafness is generally defined as a 70 dB hearing loss, varying depending on region and circumstances.
- Normal hearing is classified as 0-20 dB HL, while hearing loss severity ranges from mild (26-40 dB) to profound (>90 dB HL).
- Untreated hearing loss affects 360 million people globally and costs nearly $750 billion annually.
- An annual investment of less than US$ 1.40 per person is required to scale up global ear and hearing care services.
- Nearly 80% of people with disabling hearing loss reside in low- and middle-income countries, and the prevalence increases with age, with over 25% of those over 60 experiencing disabling hearing loss.
(Source: World Health Organization, Mastermind Behavior)
Global Aging Population
About one-third of older adults have hearing loss, and the risk increases with age. This is due to the natural aging of the auditory system and age-related changes in the inner ear and auditory nerve. Additionally, older adults are more likely to have conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, which can also contribute to hearing loss.
- In 2022, the global average life expectancy was 73.6 years, projected to rise to around 78.1 years by 2050, driven by reduced deaths from respiratory infections, cardiovascular diseases, tuberculosis, and maternal and neonatal complications.
- The U.S. population aged 65 and older is projected to grow by 47%, from 58 million in 2022 to 82 million by 2050. This increase, from 17% to 23% of the total population, is driven by healthcare advancements and longer life expectancies.
- In 2023, several persons aged 65 years and older were million in Canada.
- In 2024, the estimated population of the EU reached 449.3 million, with over one-fifth (21.6%) of people being 65 years or older.
- India, even though it has the largest youth population, is witnessing rapid progression in its aging demographic. In 2023, 153 million people aged 60 and above were in India. This number is expected to increase to 347 million by 2050.
- In 2022, Latin America and the Caribbean had 88.6 million people aged 60 and older, representing 13.4% of the population. By 2030, this proportion is expected to rise to 16.5%. Driven by improved living standards and better healthcare access.
[Source: World Health Organization (WHO), Market.us, United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), Population Reference Bureau, Government of Canada, European Union, Statista, Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC)]
Hearing Loss Classification Based on Decibel Levels
| Decibel Level (dB) | Classification | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 – 25 | Normal Hearing | Able to hear sounds within this range clearly without difficulty. |
| 26 – 40 | Serious Hearing Loss | Difficulty hearing soft sounds, especially in noisy environments. |
| 41 – 55 | Modest Hearing Loss | Struggles to understand conversations without hearing aids or amplification. |
| 56 – 70 | Modest to Severe Hearing Loss | It requires hearing devices for effective communication; it may rely heavily on lip reading. |
| 71 – 90 | Serious Hearing Loss | Can only hear loud sounds or speech when very close. |
| 91+ | Profound Hearing Loss | No ability to hear even loud sounds, often classified as legally deaf. |
What is the typical range for normal hearing?
Normal hearing generally ranges between 0-20 dB HL (Decibel Hearing Level).
| Degree of Hearing Loss | Range (dB HL) | Impact on Daily Life |
|---|---|---|
| Slight | 26-40 dB HL | Difficulty understanding speech, particularly in noisy environments. |
| Moderate | 41-55 dB HL | Regular difficulty following conversations. |
| Significant | 56-70 dB HL | Frequent reliance on lip reading for communication. |
| Severe | 71-90 dB HL | Communication primarily depends on sign language or visual cues. |
| Extreme | Greater than 90 dB HL | Very limited or no hearing, often requiring assistive hearing devices. |
(Source: Mastermind Behavior)
Global and Regional Insights
The U.S.
- In 2023, approximately 48 million Americans experienced hearing loss, reflecting the widespread nature of the condition across the population.
- Around 2 to 3 out of every 1,000 children in the U.S. (0.002% of the population) are born with hearing loss, highlighting the early onset of hearing impairment in a small but notable segment of the population.
- Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, affects about 50 million Americans, with 90% of those also experiencing some degree of hearing loss.
- Around 2 to 3 out of every 1,000 newborns in the U.S. have detectable hearing loss in one or both ears, underscoring the critical need for early detection and intervention.
- Approximately 15% of U.S. adults (37.5 million) aged 18 and older report experiencing hearing difficulty, indicating that hearing issues are common across a wide range of age groups.
- Disabling hearing loss impacts approximately 2% of adults aged 45 to 54, with the percentage rising to 8.5% among adults aged 55 to 64, showing a clear age-related trend in hearing loss.
- Over 30% of people aged 65 to 74 suffer from hearing loss, and this figure rises to more than 50% for those aged 75 and older, demonstrating a significant increase in hearing impairment with age.
Other Stats
- More than 90% of children with hearing loss are born to hearing parents, emphasizing the importance of early hearing screenings and interventions for newborns.
- Men are nearly twice as likely as women to experience hearing loss between the ages of 20 and 69, highlighting a gender disparity in hearing health.
- For adults between the ages of 20 and 69, age is the primary factor influencing hearing loss, with the most pronounced hearing impairment observed in those aged 60 to 69.
- Non-Hispanic black adults have the lowest rates of hearing loss among those aged 20 to 69, while non-Hispanic white adults are more likely to experience hearing loss compared to other racial and ethnic groups.
- Approximately 28.8 million U.S. adults could benefit from hearing aids, indicating a substantial need for increased awareness and access to hearing aid solutions.
- Disabling hearing loss affects about 25% of adults aged 65 to 74 and 50% of those aged 75 and older, underlining the considerable impact of hearing loss on older adults.
- According to standard hearing tests, 1 in 8 people in the U.S. (13% or 30 million) aged 12 years and older have hearing loss in both ears, showing the extensive reach of the condition across various age groups.
(Source: Hearing Loss Association of America, Cross River Therapy)
Canada
- Over 1.6 million people aged 15 and older, or 5.6% of the population, had a hearing disability in 2022.
- 23% of people with a hearing disability needed a hearing aid but did not have one, with 72% citing cost as the main barrier.
- Hearing disabilities were most common in the older age group of 65 years and above, affecting 13.6%, followed by 5.4% in the 45-64 years group, 2.4% in the 25-44 years group, and 1.5% in the 15-24 years group.
(Source: Government of Canada)
Europe
- In the European region, approximately 190 million people experience hearing loss or deafness, making up 20% of the population.
- In 2024, approximately 59 million Europeans experienced hearing loss that impacted their daily communication.
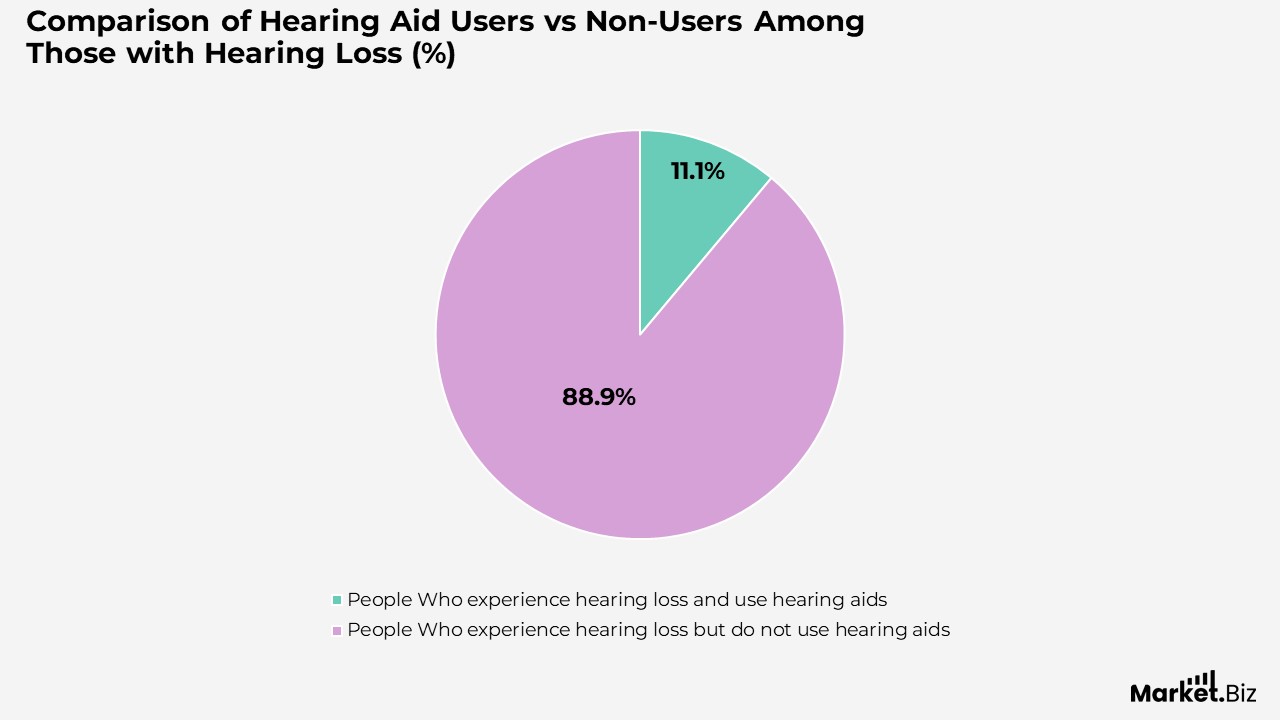
- Only 22% of those affected use hearing aids, highlighting a significant unmet need for hearing care in Europe.
- Users of hearing aids report greater satisfaction, improved well-being, higher social participation, and better income compared to non-users with hearing loss.
- Reimbursement policies for hearing aids and related services differ widely across Europe, ranging from full coverage to none.
- There is a positive relationship between the level of reimbursement and the adoption rate of hearing aids, suggesting that financial barriers prevent many from accessing necessary hearing care in Europe.
(Source: European Federation of Hard of Hearing (EFHOH))
U.K.
- Hearing loss in the U.K. is on the rise due to factors such as an aging population, exposure to noise in both work and recreational settings, and the increasing prevalence of conditions like diabetes.
- In 2023, 1 in 3 adults in the U.K. faced hearing loss, deafness, or tinnitus, with over 18 million adults affected by these conditions.
- The probability of hearing loss increases with age, with more than half of people aged 55 and older in the U.K. experiencing some form of hearing impairment.
- By age 70, approximately 80% of people will experience hearing loss, reflecting the growing prevalence of hearing issues among older adults.
- Around 1.2 million adults in the U.K. have hearing loss severe enough to make understanding most conversational speech difficult, significantly impacting daily communication for those affected.
- Around 6.7 million people in the U.K. could benefit from hearing aids, but only about 2 million currently use them.
- Approximately 900,000 people in the U.K. are severely or profoundly deaf.
- Around 12,000 people in the U.K. are using cochlear implants.
(Source: Royal National Institute for Deaf People, Hearing Link Services)
India
- In 2023, approximately 63 million people in India suffered from significant auditory impairment, making early identification of hearing loss and ear diseases crucial for effective management.
- The prevalence of hearing loss is notably higher among adults aged 60 and above in India, highlighting the impact of aging on hearing health.
- Around 67% of adults aged 40-59 years in India experience hearing loss, demonstrating the widespread nature of the condition in middle-aged adults.
- Hearing loss is higher in rural areas, with 32.4% affected, compared to 26.1% in urban areas, indicating a regional disparity in hearing health.
- Among those with hearing loss in India, approximately 30% have mild hearing loss, 13.7% have moderate hearing loss, and 51.2% experience severe hearing loss, indicating a significant portion of the population with more severe impairments.
(Source: World Health Organization, Indian Express, main.mohfw, hear-it )
Australia
- Approximately 3.6 million Australians are affected by hearing loss, which is expected to double by 2050.
- In 2021-2022, Hearing Australia assisted more than 270,000 children and adults in managing hearing loss.
- One in five children in Australia had a middle ear infection in 2022, a common issue that can impact hearing.
- 6% of children in Australia visited ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists, reflecting the need for specialized care in hearing health in 2022.
- Hearing Australia provided services to 29,908 young Australians under 21, addressing early hearing challenges from 2021 to 2022.
- Hearing Australia also supported 5,086 young adults between the ages of 21 and 26, providing crucial hearing services during a pivotal age range.
- In 2021-2022, 29,629 adults with complex hearing needs received services from Hearing Australia, demonstrating the wide-ranging impact of hearing loss across all ages.
(Source: Hearing Australia, Market.us)
Latin America
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), hearing loss affects a large segment of the population in Latin America, with millions experiencing varying levels of auditory impairment.
- In 2023, approximately 217 million people in Latin America are living with hearing loss, highlighting the widespread nature of the condition across the region.
- Of this population, about 62.7 million people suffered from moderate to severe hearing loss, underlining the significant impact of hearing impairment in the region.
- The number of people with hearing loss in Latin America is projected to rise to 332 million by 2050. Signaling an increasing public health concern.
- In Brazil, the prevalence of hearing loss among children is particularly high, with around 30% affected, indicating the critical need for early intervention and preventive measures in younger populations.
- Over 1.5 million people in Chile are affected by hearing loss. Illustrating the substantial number of individuals impacted by this condition.
- In Costa Rica, about 1,000 children are born with hearing loss annually, emphasizing the importance of early detection and support for newborns with hearing impairments.
(Source: World Health Organization, Pan American Health Organization)
The Cost of Hearing Loss
The economic impact of hearing loss is substantial, with global costs exceeding $981 billion due to reduced quality of life, healthcare expenses, and lost productivity. In Europe, untreated hearing loss costs around €216 billion annually, while in the U.S., the figure is about $133 billion.
People with hearing loss often experience lower incomes, with untreated cases reducing earnings by up to $12,000 per year. Additionally, hearing loss is linked to higher unemployment rates and early retirement. It also increases healthcare utilization and reliance on social services, further straining economic resources. Early detection and intervention can help mitigate these costs.
(Source: Hearing You, European Hearing Instrument Manufacturers Association (EHIMA), Insurtech Insights, Hearing Health Foundation)
Recent Developments
Product Launches
- In August 2024, Sonova Holding AG, a Swiss-based hearing care solutions company, introduced the Phonak Audéo Infinio and Audéo Sphere Infinio, two innovative hearing aid platforms, including the first hearing aid equipped with real-time AI to address the most pressing needs in hearing loss.
- In September 2024, U.S.-based hearing aid company Signia launched the Signia Active Pro IX, designed for users with moderate hearing loss, enabling them to engage in dynamic conversations and lead active, social lives even in noisy environments.
Acquisitions and Mergers
- Audiology Innovations has merged with HearWell Technologies to create a unified platform for hearing loss solutions. With projected annual revenues exceeding $300 million.
- HearingTech Inc. has acquired SoundCare Solutions for $100 million. Strengthening its foothold in the hearing aid market and broadening its product range.
Consumer Trends
- Growing awareness of hearing health and advancements in hearing aid technology have driven the demand for hearing loss solutions. Sales are increasing by 15% from the previous year.
- Sales of Bluetooth-enabled hearing aids surged by 20%, highlighting consumers’ preference for enhanced connectivity and convenience in hearing aid technology.
Regulatory Landscape
Regulatory authorities have established hearing aid performance and safety standards, ensuring compliance with quality benchmarks and protecting consumers in the hearing healthcare market.
Conclusion
Hearing Loss Statistics: Hearing loss is a growing and widespread issue, impacting millions of individuals worldwide with far-reaching social, emotional, and economic effects. It affects people of all ages, from children to seniors, with its prevalence increasing as people age. Many hearing loss patients worldwide do not receive proper care, underscoring the urgent need for increased awareness, early detection, and better access to treatments such as hearing aids and cochlear implants.
As the global burden of hearing loss continues to rise, particularly among aging populations. It is vital to focus on public health efforts, enhance accessibility to hearing care, and promote preventative strategies. By implementing effective interventions, we can improve the quality of life for those affected and reduce the broader economic burden on society.
FAQ’s
The most common cause of hearing loss is exposure to loud noises, especially in industrialized nations. Other contributing factors include aging, genetic predispositions, certain medications, infections, and ear-related physical injuries.
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that approximately 1.5 billion people worldwide have disabling hearing loss, which accounts for 20% of the global population.
Hearing loss tends to be more prevalent in men compared to women, particularly in middle-aged and older populations.
The likelihood of hearing loss increases with age. It is projected that one-third of individuals aged 65 and older will experience some form of hearing loss, with over 50% of adults aged 75 and above affected by this condition.
Failing to address hearing loss can severely affect a person’s quality of life, leading to challenges in communication, social isolation, and a decline in cognitive abilities.