Introduction
Food Waste Statistics: Food statistics offer valuable insights into the global production, consumption, distribution, and trade of food products. They cover a broad spectrum of data, including agricultural yields, food availability, nutritional consumption, price trends, and indicators of food security. Reliable and up-to-date food statistics are crucial for policymakers, industry stakeholders, and researchers to understand market trends, identify challenges in supply chains, and address issues such as hunger and malnutrition.
The significance of food statistics has increased notably in recent years, driven by factors such as the growing global population, evolving dietary habits, and the impact of climate change on agricultural output. These data points enable the monitoring of fluctuations in food demand and supply, the assessment of price instability, and the evaluation of policy impacts. Furthermore, food statistics underpin sustainable development initiatives by guiding efforts to improve food safety, minimize waste, and strengthen the resilience of global food systems.
Editor’s Choice
- Globally, about 1.3 billion tonnes of food are discarded annually.
- Despite this massive waste, nearly 690 million individuals worldwide suffer from chronic hunger.
- The annual economic impact of food surplus worldwide is projected to be close to US$1 trillion.
- In developing nations, most food leftover occurs during the manufacturing and post-harvest phases, whereas in developed countries, the majority of waste arises at the customer level.
- Food waste significantly contributes to climate change, accounting for roughly 8% of total global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Developed countries discard nearly 222 million tonnes of food annually, almost matching the entire net food manufacture of sub-Saharan Africa, which stands at 230 million tonnes.
- Food wastage exacerbates the issue of worldwide water shortages, with nearly 24% of all agricultural water being lost through wasted food.
- In the U.S. alone, approximately 30 to 40% of the food supply is wasted each year, equivalent to roughly 133 billion pounds of food valued at around US$ 161 billion.
(Source: Market.us, FAO)
Global Smart Food Bin Market Size
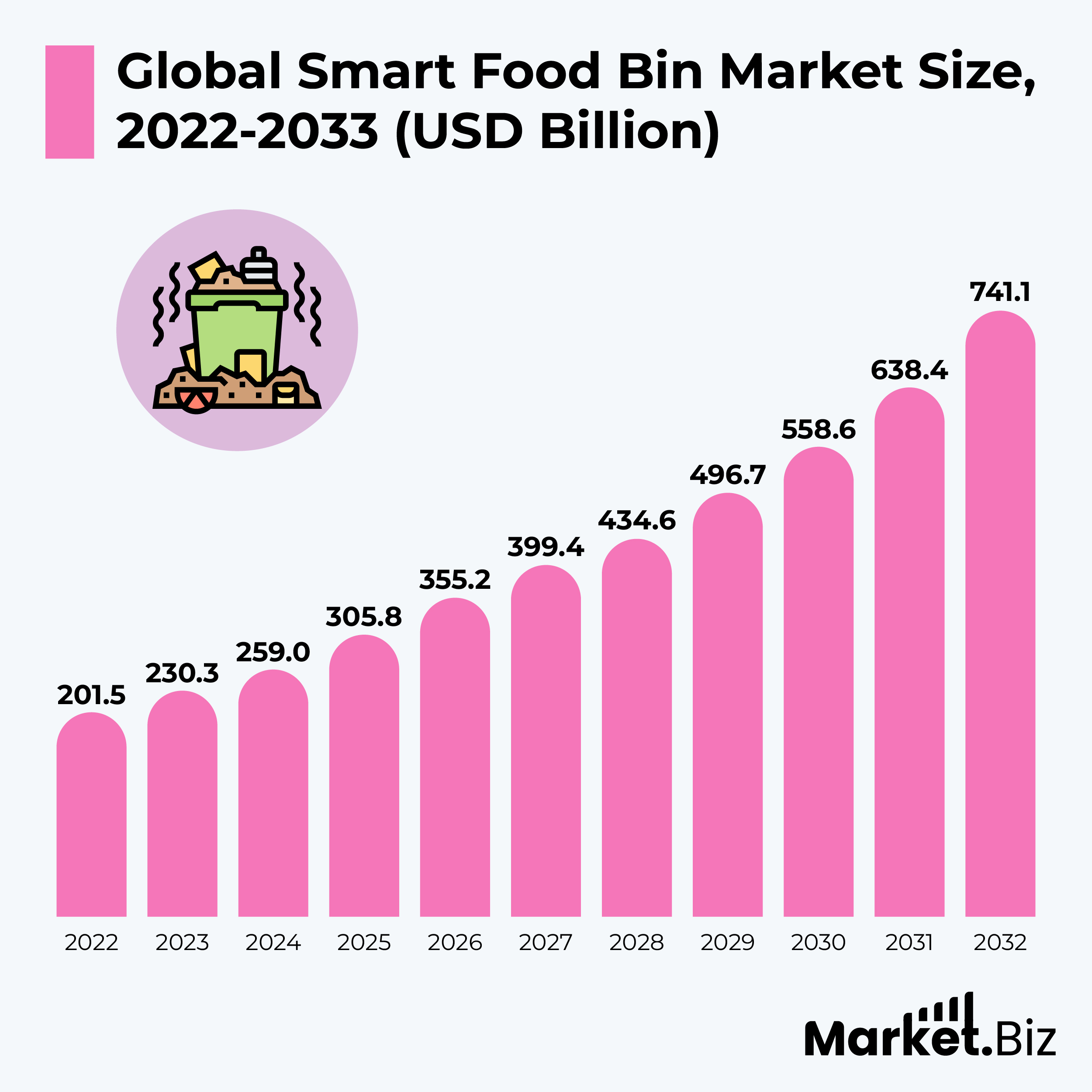
- According to Market.us, the global smart food bin market is projected to grow from $305.8 billion in 2025 to $741.7 billion by 2032, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.3% from 2022 to 2032.
- The market’s expansion is driven by increasing urbanization, rising global food waste, and growing public awareness about food waste.
- In 2022, the automatic segment dominated the Smart Food Bin Market, capturing a significant 65% revenue share. These automatic bins are gaining widespread favour across various food service sectors due to their advantages, including enhanced efficiency, improved productivity, and the ability to manage large volumes of food waste effectively. These benefits are expected to continue driving the segment’s growth during the forecast period.
- The multi-compartment segment exhibited the fastest growth in 2022, with a revenue share of 55.4%. These bins, designed with separate compartments for different types of food waste, often incorporate sensors that detect the type of waste and sort it accordingly, thereby improving waste disposal efficiency.
- Offline sales channels led the Smart Food Bin Market in 2022, accounting for 51% of global revenue. Factors such as consumer hesitation toward online purchases and the widespread availability of advanced smart bins through wholesale and speciality stores contribute to this trend.
- The commercial end-user segment is projected to lead with the largest revenue share of 57% in 2022, driven by the rapid growth of commercial food establishments, including restaurants and grocery stores worldwide.
- North America is anticipated to hold the largest market share, at 35%, generating revenues of approximately US$70.5 million during the forecast period, primarily due to heightened consumer awareness about reducing food waste.
- Europe is expected to experience substantial growth throughout the forecast timeline, supported by the presence of key market players. Countries such as Spain, Germany, France, and the UK generate substantial amounts of food waste, which is likely to increase demand for smart food bins.
- Additionally, regional efforts to reduce food waste by adopting innovative solutions, such as converting waste into compostable materials, are expected to stimulate market growth further.
(Source: Market.us)
Global Food Waste Statistics
Food waste represents a significant global issue, impacting food security and environmental sustainability. The scale and consequences of this problem underscore the need for urgent intervention and innovation.
- Globally, the volume of food discarded each year equals roughly one-third of all food formed for human intake.
- Affluent regions such as Europe and North America experience higher per capita food waste compared to lower-income areas, reflecting differing consumption patterns and waste management practices.
- Industrialized nations annually discard approximately 222 million tons of food, a figure nearly equivalent to the total net food production of sub-Saharan Africa, which stands at 230 million tons.
- Food waste is responsible for nearly 8% to 10% of worldwide greenhouse gas releases. If it were considered a state, it would rank as the third-largest emitter after the United States and China.
- Approximately 1.4 billion hectares of agricultural land, around 30% of the world’s total farmland, are used to produce food that ultimately goes to waste.
- The water embedded in wasted food amounts to nearly 250 cubic kilometers per year, a volume comparable to the annual discharge of Europe’s largest river, the Volga.
- Households are the largest contributors, generating an estimated 569 million tonnes of food surplus worldwide.
- The retail sector accounts for approximately 244 million tonnes of the global food waste figures.
- Food service production is also a significant contributor, with approximately 118 million tonnes of food wasted worldwide each year.
(Source: Stop Wasting Food, MDPI, Journal of Resources and Ecology, Food and Agriculture Organization, Statista)
Food Waste in Worldwide in 2022
| SECTOR | GLOBAL AVERAGE (KG/CAPITA/YEAR) | 2022 TOTAL (MILLION TONNES |
|---|---|---|
| Household | 79 | 631 |
| Food Service | 36 | 290 |
| Retail | 17 | 131 |
| Total | 132 | 1,052 |
(Source: UNEP)
Food Waste in the Retail Sector
Food waste generated by the retail sector remains a significant contributor to overall food loss in many countries, reflecting inefficiencies in supply chain management and consumer demand forecasting. Retailers, including supermarkets and grocery stores, play a vital role in reducing food waste worldwide.
- In the United States, the retail industry is responsible for discarding roughly 43 billion pounds (approximately 19.5 million metric tons) of food annually.
- Supermarkets and grocery stores in the United Kingdom produce around 200,000 tons of food waste every year.
- Australian supermarkets contribute an estimated 7.3 million tonnes of food waste annually, incurring costs of about AUD 36.6 billion per year.
- Retailers in Canada account for approximately 10% of the nation’s total food waste, according to recent surveys.
- In South Africa, food waste from retailers amounts to approximately 2.8 million tons annually.
- China experiences the loss or waste of more than 35 million tonnes of food annually, representing roughly six per cent of the country’s total food production, enough to nourish between 30 and 50 million people.
(Source: Global Voices, Waste Managed, Government of Canada, IFAD, World Resources Institute)
Food Waste in Households
- The household segment accounts for about 62% of total global food waste.
- In high-income countries, households leave about 95 to 115 kg of food per capita per year.
- The per capita household food surplus in middle- and low-income countries ranges from 6 to 11 kg annually.
- Approximately 40% of food unused by homes is vegetables and fruits.
- Cereals and bread contribute to about 20% of household food leftover.
- Dairy products, such as cheese and milk, account for roughly 17% of household food waste.
- Fish and meat waste make up approximately 8-10% of household food waste.
- Leftover and prepared meals account for roughly 8% of food waste in households.
- In high-income countries, consumers dispose of about 10 to 15% of their food consumption.
- Improper meal planning and a lack of awareness are significant contributors to household food waste.
(Source: Research Gate, Food and Agriculture Organization, Bluebookservices, ResearchGate, UNFCCC)
Food Waste in the Food Service Industry
- The food service industry is responsible for about 10% of the world’s total food waste.
- Approximately 5% of the global food production is lost within this sector.
- In restaurants and catering businesses, food waste can represent nearly 14% of their overall operating costs.
- In the United States alone, the food service sector generates more than 11 million tons of food waste annually.
- On average, restaurants and food service establishments discard between 4% and 10% of the food they purchase.
- Buffet-style dining operations tend to generate more food waste compared to other food service formats.
- Key causes of food waste in this sector include excess food production, spoilage, and uneaten portions left on plates.
- Nearly 40% to 50% of fruits and vegetables served in the food service industry end up being wasted.
- In Europe, the food service sector accounts for approximately 14% of the total food waste generated throughout the entire supply chain.
- Adopting food waste reduction measures within the U.S. food service sector has the potential to save businesses up to $1.6 billion annually.
(Source: Environmental Protection Agency, World Resources Institute, European Commission)
Financial Impact of Food Waste
- Globally, food waste results in an estimated economic loss of nearly $ 1 trillion per year.
- In wealthy nations, the annual financial burden of food waste reaches around US$680 billion, whereas in low- and middle-income countries, the cost is approximately US$310 billion.
- Throughout the supply chain, food waste results in considerable monetary losses for farmers, manufacturers, and retailers, with estimates indicating that 15% to 30% of the total production value is lost.
- The hospitality industry faces notable economic setbacks due to food wastage, with restaurants and catering businesses losing up to 4% of their profits because of discarded food.
- Investing in effective food waste reduction strategies yields significant financial returns; on average, every dollar spent on such initiatives results in approximately $14 in cost savings.
(Source: Food Waste Reduction Alliance, FAO, World Bank)
Cost Savings Through Reducing Food Waste
According to ReFED, a sustained annual investment of $14 billion in food waste reduction initiatives over the next decade in the United States could yield significant benefits:
- Decrease food waste by 45 million tons each year
- Generate a net financial gain of $73 billion annually for the nation
- Cut greenhouse gas emissions by 75 million metric tons and provide the equivalent of four billion meals annually to those facing food insecurity.
- Support the creation of 51,000 new jobs over ten years
- Meet the 2030 national target of halving the volume of wasted food
(Source: Divert)
Food Waste Statistics – By Country/Region
Regional Average Household Waste per Person Annually (kg)
| Region | Number of Countries Reporting | Average Household Waste Generation (kg/year) |
|---|---|---|
| Northern Africa | 3 | 140 |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 14 | 93 |
| Latin America & Caribbean | 10 | 95 |
| Northern America | 2 | 76 |
| Eastern Asia | 5 | 70 |
| South-eastern Asia | 8 | 70 |
| Southern Asia | 7 | 100 |
| Western Asia | 9 | 116 |
| Eastern Europe | 6 | 53 |
| Northern Europe | 9 | 69 |
| Southern Europe | 8 | 83 |
| Western Europe | 7 | 80 |
| Australia & New Zealand | 2 | 79 |
| Melanesia | 2 | 92 |
| Micronesia | 1 | 38 |
(Source: United Nations Environment Programme)
Food Waste Statistics in North America – By Sectors
| Country | Sector | Food Wastage Estimate (Kg/Capita/Year) |
|---|---|---|
| Canada | Household | 79 |
| Food Service | 80 | |
| Retail | 30 | |
| The U.S. | Household | 73 |
| Food Service | 74 | |
| Retail | 12 |
(Source: United Nations Environment Programme)
- China and India, being the world’s two most populous nations, were among the top contributors to food waste in 2022, producing approximately 109 million and 78 million metric tons, respectively.
- According to a 2022 survey, 61% of consumers believe that brands, retailers, and supermarkets should intensify their efforts to reduce food waste, while 57% expressed dissatisfaction with the current measures in place.
- Leading supermarket chains in the UK, including Tesco, Sainsbury’s, Asda, and Morrisons, have pledged to meet Sustainable Development Goal 12.3, aiming to halve food waste by 2030.
- UK supermarkets reportedly discard around 200,000 tonnes of food, equivalent to more than 350 million meals, annually.
- According to the United Nations Environment Programme’s Food Wastage Index, Indian households discard approximately 68.7 million tonnes of food each year, which translates to about 55 kilograms per person annually. This places India second globally in terms of household food waste, trailing only behind China.
- A study by the National Resources Defense Council (NRDC) reveals that in the United States, nearly 40% of all food created is never consumed. Meanwhile, across Asia, an estimated 1.34 billion tonnes of food are wasted annually, with India and China identified as the primary contributors to this significant loss.
(Source: Statista, Waste Managed, Times of Agriculture)
Conclusion
Food waste remains a significant global challenge with profound economic, environmental, and social implications. The enormous quantity of discarded food, amounting to nearly one-third of total food production, reveals inefficiencies throughout the supply chain, spanning from production and retail to end consumers. The uneven distribution of waste, with high-income regions generating disproportionate amounts and considerable losses in developing countries, highlights the need for tailored approaches to address the problem effectively worldwide.
Additionally, the environmental consequences, including high greenhouse gas releases, extensive land use, and water wastage, stress the critical need for sustainable food management solutions. Tackling food waste presents a dual opportunity to enhance food security and alleviate hunger while also mitigating climate change and conserving vital natural resources. Achieving substantial progress requires collaborative action from policymakers, businesses, and consumers to reduce food loss and foster a more sustainable food system globally.
FAQ’s
Every year, approximately 1.3 billion metric tons of food are discarded worldwide, accounting for about one-third of the total food produced for human consumption.
Food waste per capita is significantly higher in high-income areas, such as North America and Europe, compared to lower-income regions. Developed nations waste nearly as much food as the total food production of some entire continents.
Food waste is responsible for approximately 8% of worldwide greenhouse gas emissions, making it a notable contributor to climate change.
Discarded food uses about 1.4 billion hectares of agricultural land. It leads to the wastage of around 250 cubic kilometres of water annually, which is comparable to the yearly flow of Europe’s largest river.
Globally, households account for the majority of food waste (around 569 million tonnes), followed by the retail sector (about 244 million tonnes) and the food service industry (approximately 118 million tonnes).
In developed countries, most food waste occurs at the consumer level due to reasons such as overbuying, improper storage, and strict aesthetic standards. Conversely, in developing countries, food loss is mainly due to inefficiencies in production and post-harvest handling.
The global economic loss due to food waste is estimated to be around US$1 trillion annually, encompassing wasted resources, labor costs, and environmental damages.
